🧬 کاربرد اکسید آلومینیوم در دارورسانی هدفمند و ایمپلنتهای زیستسازگار
✳️ مقدمه:
در سالهای اخیر، اکسید آلومینیوم (Al₂O₃) بهدلیل خواص فیزیکی، شیمیایی و زیستی منحصربهفرد، بهعنوان یک گزینه مؤثر در حوزه پزشکی و فناوریهای زیستپزشکی مورد توجه قرار گرفتهاند. این نانوذرات با داشتن پایداری بالا، زیستسازگاری قابل قبول و قابلیت اصلاح سطح، برای سیستمهای دارورسانی هدفمند و ایمپلنتهای مهندسی بافت، بسیار امیدوارکننده هستند.
⚙️ ویژگیهای کلیدی نانوذرات آلومینا برای کاربرد زیستی:
-
زیستسازگاری (Biocompatibility): بافت بدن واکنش نامطلوبی نسبت به آلومینا نشان نمیدهد، بهویژه در فرم نانوساختار.
-
پایداری شیمیایی: در برابر تخریب شیمیایی و محیطهای اسیدی و قلیایی مقاوم است.
-
نرمی سطح (Smoothness) و قابلیت اصلاح: امکان پوششدهی با پلیمرهای زیستی یا عاملهای دارویی برای رسانش هدفمند فراهم است.
-
فعالیت سطحی بالا: بهدلیل سطح ویژه زیاد، امکان بارگذاری مؤثر داروها یا مولکولهای زیستی را دارد.
💊 کاربرد نانوذرات آلومینا در دارورسانی هدفمند (Targeted Drug Delivery)
✅ مقدمه کاربردی:
دارورسانی هدفمند یکی از چالشبرانگیزترین و درعینحال امیدبخشترین حوزههای فناوری نانو در پزشکی نوین است. هدف اصلی آن، تحویل انتخابی دارو به بافت یا سلولهای خاص در بدن است، بهطوری که اثر درمانی حداکثری و عوارض جانبی حداقلی حاصل شود. اکسید آلومینیوم (Al₂O₃) به دلیل خواص ویژه خود، از جمله پایداری شیمیایی، سطح ویژه بالا، امکان عملکرددهی سطحی و زیستسازگاری نسبی، به عنوان حاملهای دارویی در این زمینه مورد توجه هستند.
⚙️ مزایای نانوآلومینا برای دارورسانی هدفمند:
-
قابلیت اصلاح سطح (Surface Functionalization):
نانوذرات آلومینا میتوانند به راحتی با پلیمرها، لیگاندها، آنتیبادیها یا مولکولهای زیستی کووالانسی یا غیرکووالانسی پیوند یابند. این ویژگی باعث میشود ذره بتواند بهصورت هدفمند به گیرندههای خاص روی سلولهای سرطانی یا بافت آسیبدیده متصل شود. -
آزادسازی کنترلشده دارو (Controlled Release):
ساختار متخلخل یا اصلاحشده اکسید آلومینیوم امکان بارگذاری دارو و آزادسازی تدریجی آن در محیطهای خاص (مثلاً محیط اسیدی داخل تومورها) را فراهم میسازد. -
پایداری در شرایط فیزیولوژیکی:
برخلاف برخی حاملهای نانوپلیمری، آلومینا در برابر تجزیه آنزیمی یا تخریب سریع در خون و مایعات بدن مقاومت خوبی دارد.
🎯 مکانیسم عملکرد هدفمند:
اکسید آلومینیوم با دارو بارگذاری میشوند و سطح آنها با مولکولهای شناساییکننده مانند آنتیبادی یا فولات پوشش داده میشود. این مولکولها به گیرندههای خاص روی سطح سلولهای هدف (مثلاً سلولهای توموری که گیرنده فولات دارند) متصل میشوند. پس از اتصال، ذره توسط فرآیند اندوسیتوز وارد سلول میشود و دارو درون سلول آزاد میشود.
🧪 نمونههای تجربی و کاربردی:
-
درمان سرطان پستان: اکسید آلومینیوم اصلاحشده با لیگاندهای ضد-HER2 برای رساندن داروهای شیمیدرمانی مانند دوکسوروبیسین به سلولهای سرطان پستان.
-
دارورسانی ضدالتهابی: استفاده از اکسید آلومینیوم برای حمل داروهایی مانند دگزامتازون در درمان بیماریهای مزمن التهابی.
-
رسانش آنتیبیوتیکها: برای غلبه بر مقاومت باکتریایی و رساندن دارو به نواحی عفونی خاص، خصوصاً در عفونتهای استخوانی و مفصلی.
⚠️ چالشهای پژوهشی:
-
ارزیابی دقیق سمیت مزمن و بیخطر بودن در دوزهای بالا
-
کنترل بر اندازه و توزیع اندازه ذرات (Size Distribution) برای کاهش تجمع در کبد و طحال
-
نیاز به بررسیهای بالینی و انسانی برای انتقال از آزمایشگاه به بازار
🔭 آینده و چشمانداز:
با توسعه نانوآلومیناهای هوشمند با پاسخدهی به محرکهای خاص (pH، دما، آنزیم)، امکان طراحی سیستمهای دارورسانی نسل جدید با دقت بالا در تحویل دارو فراهم خواهد شد. همچنین تلفیق نانوآلومینا با مواد مغناطیسی یا فلورسانس میتواند برای رصد تصویری مسیر دارورسانی در بدن مورد استفاده قرار گیرد.
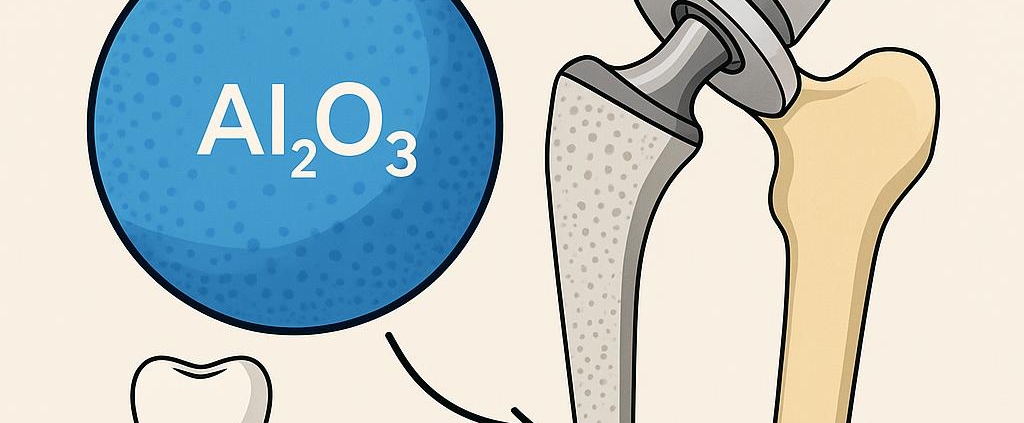
🦴 کاربرد نانوذرات آلومینا در ایمپلنتهای زیستسازگار (Biocompatible Implants)
🧩 مقدمه:
ایمپلنتهای زیستی، بهویژه در حوزه ارتوپدی، دندانپزشکی، و مهندسی بافت، نیازمند موادی هستند که علاوه بر دارا بودن استحکام مکانیکی مناسب، از زیستسازگاری، مقاومت شیمیایی، و پایداری بلندمدت در بدن برخوردار باشند. اکسید آلومینیوم (Al₂O₃) به عنوان یک مادهی سرامیکی خنثی و غیرسمی، با قابلیت یکپارچگی با بافتهای بدن (biological integration)، در ساخت یا پوششدهی ایمپلنتهای زیستسازگار بسیار کاربردی شدهاند.
✅ ویژگیهای مطلوب نانوآلومینا برای ایمپلنتها:
-
سختی و مقاومت سایشی بالا:
آلومینا یکی از سختترین سرامیکهاست، که موجب افزایش دوام و عمر ایمپلنت در شرایط مکانیکی میشود. -
زیستسازگاری اثباتشده:
آلومینا هیچ واکنش ایمنی یا التهابی قابلتوجهی در محیط بدن ایجاد نمیکند، و از نظر FDA در برخی کاربردهای زیستی تأیید شده است. -
مقاومت به خوردگی و تخریب زیستی:
برخلاف فلزات، آلومینا دچار خوردگی در محیطهای بیولوژیکی نمیشود، که این ویژگی برای جلوگیری از آزاد شدن یونهای مضر حیاتی است. -
سطح مناسب برای رشد سلولی (Osteoconduction):
سطح نانوآلومینا، به ویژه در صورت اصلاح با پوششهای زیستی (مانند هیدروکسیآپاتیت)، میتواند باعث چسبندگی بهتر سلولهای استخوانی شود.
🔬 کاربردهای کلیدی:
1. ایمپلنتهای ارتوپدی:
-
در ساخت سر مفصل لگن (hip prosthesis) و اجزای جایگزین مفصل زانو
-
کاهش سایش بین اجزای ایمپلنت و استخوان
-
افزایش ثبات مکانیکی و کاهش نیاز به تعویض در بلندمدت
2. ایمپلنتهای دندانی:
-
استفاده بهعنوان پایه ایمپلنت یا روکش مقاوم روی فلزات
-
کاهش انتقال استرس به استخوان فک
-
جلوگیری از واکنش التهابی لثهها
3. پوششدهی سطح ایمپلنتهای فلزی با نانوآلومینا:
-
ایجاد یک لایه محافظ برای کاهش واکنشهای الکتروشیمیایی
-
افزایش چسبندگی سلولی و ایجاد پیوند بهتر با استخوان
-
جلوگیری از آزادسازی یونهای فلزی سمی مثل نیکل یا کروم
🧪 نوآوریهای ترکیبی:
-
آلومینا + هیدروکسیآپاتیت (HA):
ترکیب این دو ماده میتواند هم خواص مکانیکی (از آلومینا) و هم ویژگیهای زیستی (از HA) را بهبود بخشد. -
آلومینا در قالب کامپوزیتهای هوشمند:
ترکیب با پلیمرهای زیستتخریبپذیر برای ایمپلنتهای موقتی که بهمرور جایگزین بافت طبیعی میشوند.
⚠️ چالشها و ملاحظات:
-
شکنندگی ذاتی آلومینا در ابعاد بزرگ (مناسبتر برای پوششها یا اجزای کوچک)
-
نیاز به طراحی سطح با تخلخل مناسب برای افزایش چسبندگی زیستی
-
بررسی تعامل درازمدت با بافت در شرایط بالینی (in vivo studies)
🔭 آیندهپژوهی:
پیشرفت در ساختاردهی اکسید آلومینیوم با الگوهای زیستی (bio-mimetic designs)، و استفاده از فناوری چاپ سهبعدی زیستی (3D bioprinting) میتواند منجر به طراحی ایمپلنتهای هوشمند با ویژگیهایی مانند پاسخپذیری به تحریکات مکانیکی یا زیستی شود. همچنین، اتصال نانوذرات آلومینا با فاکتورهای رشد سلولی یا داروهای ضدالتهابی میتواند باعث تسریع ترمیم بافت و جلوگیری از عفونت شود.
📈 چالشها و چشماندازها:
با وجود مزایای متعدد، هنوز چالشهایی مانند موارد زیر وجود دارد:
-
بررسی دقیق ایمنی درازمدت نانوذرات آلومینا در بدن
-
کنترل دقیق بر اندازه، سطح، و بارگذاری دارو
-
بهینهسازی روشهای سنتز برای تولید صنعتی و اقتصادی
با پیشرفتهای آینده در حوزه نانوفناوری، انتظار میرود آلومینای نانوساختار، نقش مهمتری در درمانهای دقیق و پزشکی بازساختی ایفا کند.
📚 منابع پیشنهادی برای پژوهش بیشتر:
-
Zhang, L., et al. (2020). Biomedical applications of alumina nanoparticles: A review. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research.
🧬 Applications of Aluminum Oxide in Targeted Drug Delivery and Biocompatible Implants
✳️ Introduction:
In recent years, aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) has gained considerable attention in the medical and biomedical technology fields due to its unique physical, chemical, and biological properties. These nanoparticles, with high stability, acceptable biocompatibility, and surface modifiability, are highly promising for targeted drug delivery systems and tissue-engineered implants.
⚙️ Key Features of Alumina Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications:
-
Biocompatibility: Alumina, especially in nanostructured form, does not trigger adverse reactions in body tissues.
-
Chemical Stability: Resistant to degradation in acidic and alkaline environments.
-
Surface Smoothness and Modifiability: Can be coated with biopolymers or drug agents for targeted delivery.
-
High Surface Activity: High specific surface area enables effective drug or biomolecule loading.
💊 Application of Alumina Nanoparticles in Targeted Drug Delivery
✅ Practical Introduction:
Targeted drug delivery is one of the most challenging yet promising areas of nanotechnology in modern medicine. Its primary goal is to selectively deliver drugs to specific tissues or cells in the body, maximizing therapeutic effects while minimizing side effects. Due to its chemical stability, high surface area, functionalizability, and relative biocompatibility, aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) is being investigated as a potential drug carrier.
⚙️ Advantages of Nano-Alumina in Targeted Drug Delivery:
-
Surface Functionalization:
Alumina nanoparticles can be easily functionalized with polymers, ligands, antibodies, or biomolecules (covalently or non-covalently), allowing them to bind to specific receptors on cancer or damaged cells. -
Controlled Drug Release:
The porous or surface-modified structure of alumina allows for drug loading and gradual release in specific environments (e.g., the acidic environment of tumors). -
Stability in Physiological Conditions:
Unlike some polymeric carriers, alumina is resistant to enzymatic degradation or rapid breakdown in blood and body fluids.
🎯 Mechanism of Targeted Action:
Alumina particles are loaded with drugs and coated with targeting molecules such as antibodies or folic acid. These molecules bind to specific receptors on target cells (e.g., tumor cells with folate receptors). Once attached, the particle is internalized via endocytosis, and the drug is released inside the cell.
🧪 Experimental and Practical Examples:
-
Breast Cancer Treatment: Functionalized nano-alumina with anti-HER2 ligands used to deliver chemotherapy drugs like doxorubicin to breast cancer cells.
-
Anti-inflammatory Delivery: Alumina nanoparticles used to carry drugs like dexamethasone in the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases.
-
Antibiotic Delivery: For targeting infection sites, especially in bone or joint infections, and overcoming bacterial resistance.
⚠️ Research Challenges:
-
Accurate evaluation of chronic toxicity and safety at higher doses.
-
Size control and narrow size distribution to reduce accumulation in the liver and spleen.
-
Clinical and human trials needed for market translation.
🔭 Future Outlook:
With the development of smart nano-alumina responsive to specific stimuli (pH, temperature, enzymes), next-generation drug delivery systems with high targeting precision can be designed. Integration with magnetic or fluorescent materials can also allow real-time tracking of the drug’s journey inside the body.
🦴 Application of Alumina Nanoparticles in Biocompatible Implants
🧩 Introduction:
Biological implants—especially in orthopedics, dentistry, and tissue engineering—require materials that possess not only appropriate mechanical strength but also biocompatibility, chemical resistance, and long-term stability in the body. Aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃), a neutral and non-toxic ceramic material with excellent biological integration, has found wide application in the construction or coating of biocompatible implants.
✅ Desired Properties of Nano-Alumina for Implants:
-
High Hardness and Wear Resistance:
Alumina is one of the hardest ceramics, contributing to the durability and longevity of implants under mechanical stress. -
Proven Biocompatibility:
Alumina does not provoke immune or inflammatory responses and is FDA-approved for certain biomedical applications. -
Corrosion and Bio-Degradation Resistance:
Unlike metals, alumina does not corrode in biological environments, preventing the release of harmful ions. -
Cell Growth Support (Osteoconduction):
The surface of nano-alumina, especially when coated with bioactive materials like hydroxyapatite, enhances bone cell adhesion and growth.
🔬 Key Applications:
-
Orthopedic Implants:
-
Used in hip prostheses and knee joint replacements.
-
Reduces wear between implant parts and bone.
-
Enhances mechanical stability and long-term performance.
-
-
Dental Implants:
-
Used as implant bases or hard coatings on metals.
-
Reduces stress transmission to jawbone.
-
Prevents inflammatory reactions in the gums.
-
-
Coating of Metal Implants with Nano-Alumina:
-
Creates a protective barrier against electrochemical reactions.
-
Enhances cell adhesion and bonding with bone.
-
Prevents release of toxic metal ions like nickel or chromium.
-
🧪 Hybrid Innovations:
-
Alumina + Hydroxyapatite (HA):
Combining these materials offers enhanced mechanical properties from alumina and biological activity from HA. -
Smart Composite Implants:
Mixing nano-alumina with biodegradable polymers for temporary implants that gradually integrate into natural tissue.
⚠️ Challenges and Considerations:
-
Inherent brittleness in large dimensions (better suited for coatings or small components).
-
Need for porous surface designs to enhance bioadhesion.
-
Long-term in vivo studies required to assess interactions with tissues.
🔭 Future Perspectives:
Advancements in nano-alumina structuring with biomimetic patterns and 3D bioprinting technologies may lead to smart implants that respond to mechanical or biological stimuli. Additionally, binding nano-alumina with growth factors or anti-inflammatory drugs can accelerate tissue regeneration and prevent infections.
📈 Final Thoughts – Challenges & Outlook:
Despite its many advantages, challenges remain, including:
-
Comprehensive safety assessment of long-term use in the human body.
-
Precise control over particle size, surface characteristics, and drug loading.
-
Optimization of synthesis methods for scalable and cost-effective production.
With ongoing progress in nanotechnology, nano-structured alumina is expected to play a growing role in precision therapies and regenerative medicine.







دیدگاه خود را ثبت کنید
تمایل دارید در گفتگوها شرکت کنید؟در گفتگو ها شرکت کنید.